The highlight of Redshift 2026.2 is Texture Displacement, a new geometry-altering method that allows artists to render highly detailed surfaces directly from displacement maps while receiving near-real-time viewport feedback. Displacement is now governed by a global render-settings switch, replacing the slower, tessellation-heavy process used in earlier builds. The feature works in both GPU and CPU modes, automatically adapting to scene scale and camera distance. For production artists, this finally brings interactive sculptural surface depth comparable to native displacement workflows in offline renderers.
UV Context Projection: procedural mapping inside the shader
A new UV Context Projection node provides direct control over projection type, scale, rotation and translation inside the Redshift shading graph. It eliminates many round-trips to the DCC host for UV adjustment and supports both conventional UVs and triplanar mapping. By integrating coordinate management at shader level, the node enables consistent material behaviour across host applications such as Cinema 4D, Maya, Houdini, 3ds Max and Hydra/Solaris.

Lighting improvements and colour fidelity
Redshift 2026.2 updates its IES light implementation, letting users override light intensity either by luminous power or by peak intensity, improving physical accuracy for architectural and product-visualisation work.
The Sun and Sky model produces smoother shadows and more accurate low-angle lighting, addressing the flicker and banding visible in earlier versions. Volumetric rendering has been corrected to handle light transmission behind zero-opacity geometry, and spotlight textures now maintain sharpness when soft shadows or fog are active. Together these refinements make photometric lighting behaviour more predictable and compositing-friendly.
Broader GPU support and Metal refinement
The renderer now officially supports AMD RX 9000 Series GPUs, widening the available hardware base for Windows and macOS users. Both CUDA and Metal back-ends have been re-tuned for lower IPR latency, with improved hardware ray-tracing throughput on supported cards. On macOS, Maxon fixed instability in the texture-baking pipeline and restored full OSL shader matrix output, ensuring parity with other platforms. Artists on Apple M3 and M4 systems should see markedly fewer driver-related IPR crashes.

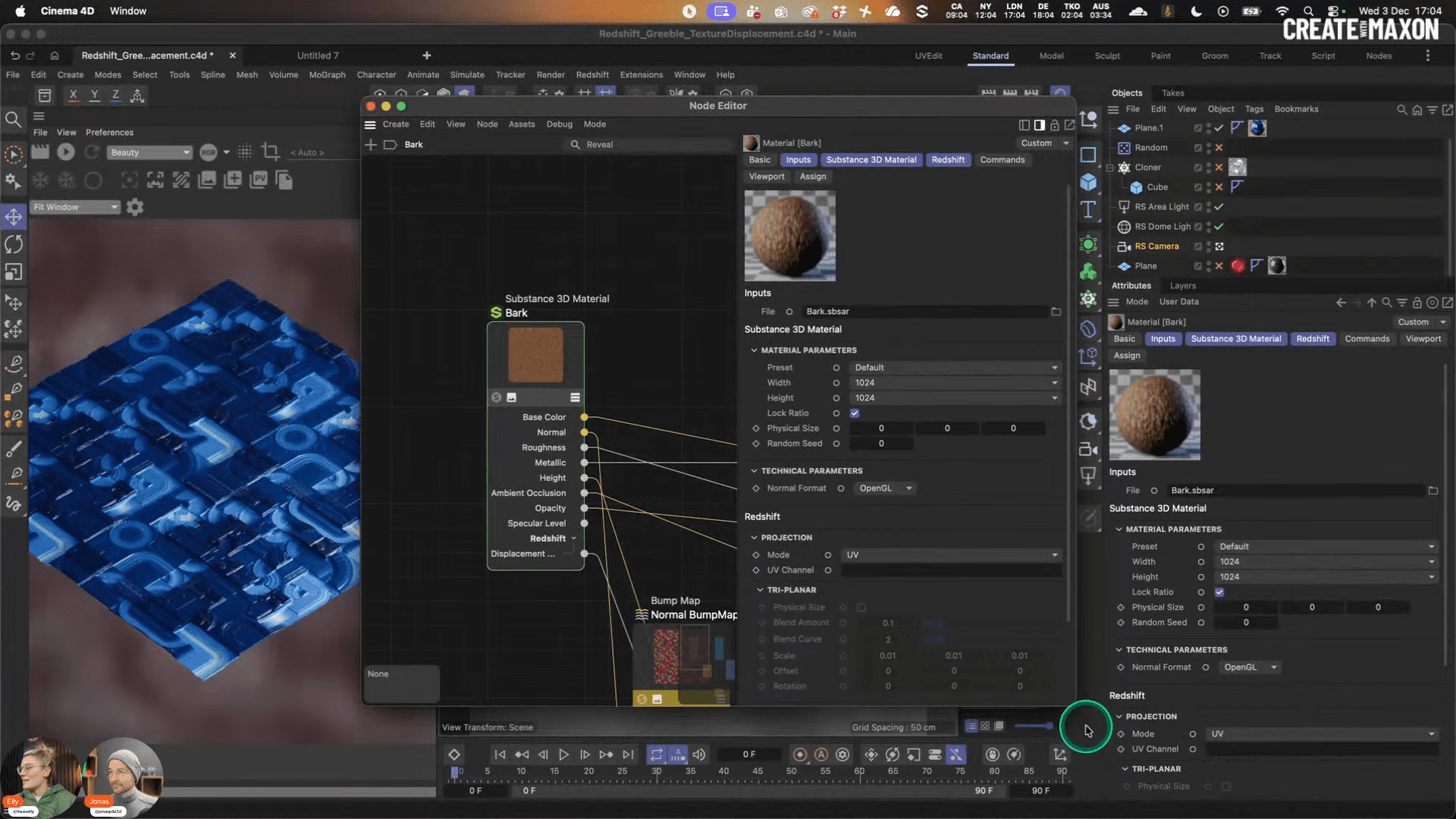
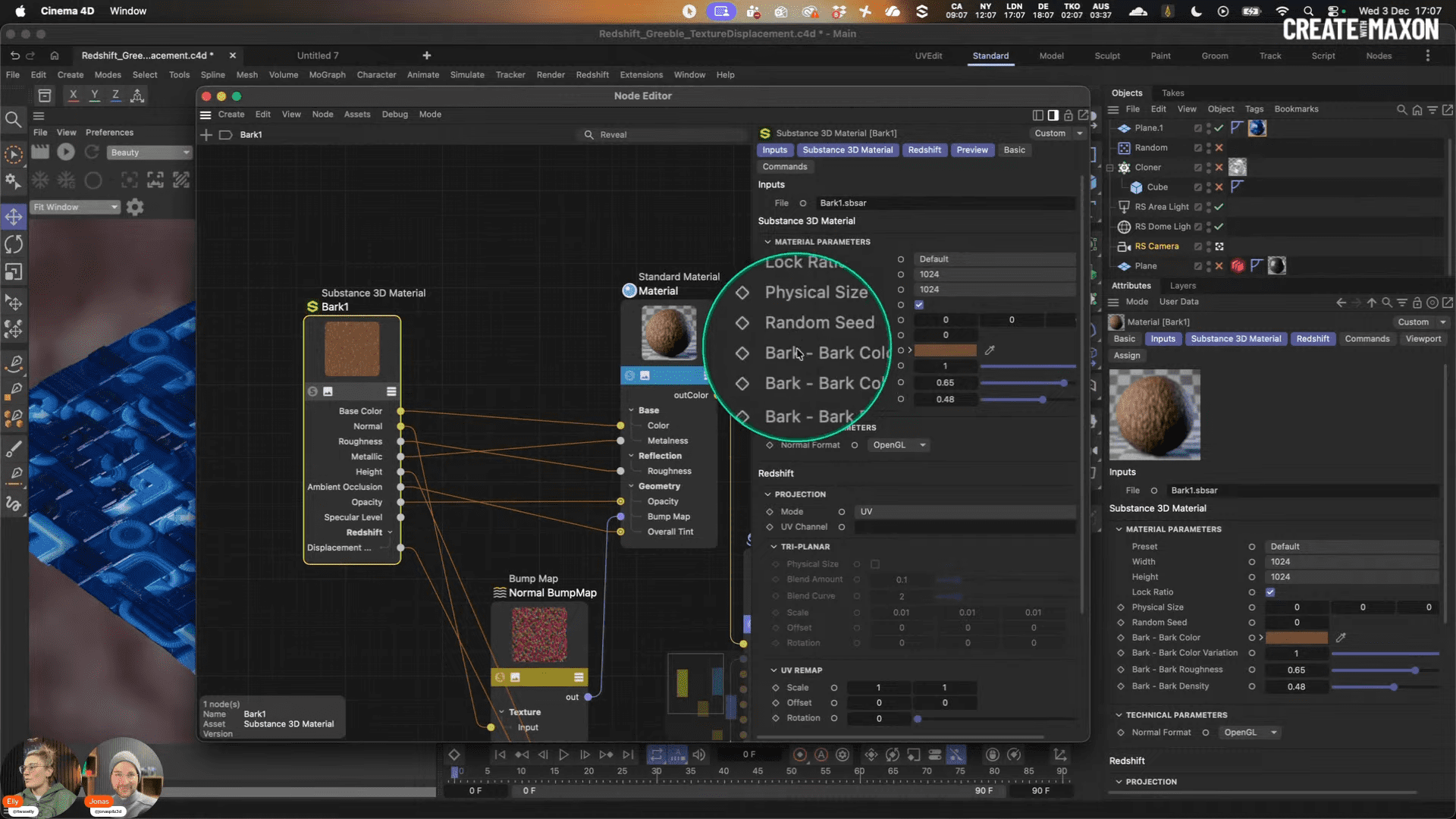
Integrated Substance access
Redshift 2026.2 introduces the Substance Sampler connector, shared with Cinema 4D 2026.1. This allows Substance textures to be imported directly into Redshift material graphs, streamlining material creation for look-development tasks and product visualisation. Exposed Parameters in Substance get also fully exposed in Cinema4D / Redshift , if you expose them before export.
Platform-wide refinements
Across DCC integrations, Redshift 2026.2 delivers smaller but practical updates. Cinema 4D gains a viewport preview light for the Sun and Sky object, new default settings for Light and Cloud primitives, and fixes to AOV handling when adding or deleting passes. Maya improves render-layer stability and updates RS Cloud defaults for more balanced scattering and transmittance. 3ds Max corrects data corruption in the RS Brick shader and adds a new default Map ID of 1 in RS Maxon Noise. Houdini and Hydra/Solaris now support version 21.0.512 while dropping legacy 20.x builds, adding Resolution Mode and husk headlight parameters to the Redshift LOP.
Engine-level reliability
The underlying renderer benefits from multiple engine-wide corrections. Shader baking has been repaired for non-centimetre scene units, and depth AOVs now respect global unit scaling. Ray Switch and cylindrical-projection bumpmapping artefacts are resolved, as are incorrect lighting results in IPR when Camera Space Render is active. Sun-sky shadow quality is improved, greyscale texture projections now output correct colour channels, and OSL shader validation blocks unsupported closure loops. Hardware Ray Tracing back-ends deliver faster interactive previews and concurrent shader-ball rendering, while IES and cloud lighting computations now yield physically consistent results.
Bug fixes and stability
The December 2025 release closes an extensive list of stability issues across all hosts. Network-stored textures no longer trigger crashes on macOS, and IPR behaviour for wind-animated RS Clouds is fixed in both Maya and 3ds Max. Volume-clipping errors caused by incorrect scene-scale calculations are corrected, and motion-blur handling for sprite baking now produces accurate results. Data corruption in older RS Brick parameters has been resolved, though affected shaders may require manual rebuilds. Together, these maintenance fixes make Redshift 2026.2 significantly more predictable for heavy-render workloads.
Availability and update guidance
Redshift 2026.2 ships with Maxon App 2025.12 and is included in all Redshift and Maxon One subscriptions.
Because this version alters displacement and shader parameter storage, studios should re-validate existing materials and test render nodes before migrating active projects.





